New Drugs and Therapies for 2016: Medical Devices
Drs. Neal Bhatia and Ted Rosen
Part 8 of an 8-part series on the large number of new topical and systemic medications that have become available or moved closer to approval in the last 12 months.
Controlling bleeding: XSTAT 30 dressing
According to the United States Army Institute of Surgical Research, 30-40% of civilian deaths by traumatic injury are the result of hemorrhaging. Of those deaths, 33-56% occur before the patient reaches a hospital. In December, 2015, the FDA cleared the use of the XSTAT 30 wound dressing, an expandable, multi-sponge dressing used to control severe, life-threatening bleeding from wounds in areas that a tourniquet cannot be placed in battlefield and civilian trauma settings. This expands the device’s indication from use by the military only to use in adults and adolescents in the general population. XSTAT 30 is cleared for use in patients at high risk for immediate, life-threatening, and severe hemorrhagic shock and non-compressible junctional wounds, when definitive care at an emergency care facility cannot be achieved within minutes. The dressing can be used for up to four hours, which could allow time for the patient to receive surgical care.
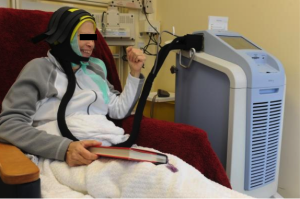
Chemotherapy-induced alopecia: Dignicap® Cooling Cap
The Dignitana DigniCap® Cooling System was approved by the FDA in December, 2015 and it is indicated to reduce the frequency and severity of alopecia during chemotherapy in breast cancer patients in which alopecia-inducing chemotherapeutic agents and doses are used. It is a computer-controlled system that circulates cooled liquid to a head-worn cooling cap during chemotherapy treatment. The cooling action is intended to constrict blood vessels in the scalp, which, in theory, reduces the amount of chemotherapy that reaches cells in the hair follicles. The cold also decreases the activity of the hair follicles, which slows cell division and makes them less affected by chemotherapy. The efficacy of this system was studied in 122 women with Stage I or II breast cancer who were undergoing chemotherapy regimens that have been associated with hair loss. The primary endpoint was a self-assessment of hair loss by the women using standardized photographs at one month after the last chemotherapy cycle. More than 66% of patients treated with the DigniCap reported losing less than half their hair. The most common side effects of the cooling system include cold-induced headaches and neck and shoulder discomfort, chills, and pain associated with wearing the cooling cap for an extended period of time.