Combined therapy using HCQ + azithromycin results in viral clearance in COVID19 infections
International J. Antimicrobial Agents in press: 17 March 2020 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949
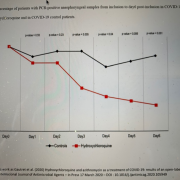
This study looked specifically at viral clearance of the nasopharynx of the SARS-CoV-2 virus using Day 6 of treatment as the 10 endpoint. Patients who tested PCR positive for SARS-CoV-2 were grouped into 3 categories: asymptomatic, upper respiratory tract infection when presenting with rhinitis, pharyngitis or isolated low-grade fever and myalgia and lower respiratory tract infections when presenting with symptoms of pneumonia and bronchitis. SARS-CoV-2 RNA was confirmed by PCR from nasopharyngeal swab. 10 endpoint was PCR confirmed nasopharyngeal swab virologic clearance at day 6. Dose of HCQ 200 mg tid x 10 days. Azithromycin was dosed prn based on clinical assessment of the treating physician.
- 42 pts: 26 treated w/ HCQ vs. 16 controls; 6 HCQ lost to f/u -> 3 sent to ICU and were PCR + through day 3 , 1 died (although PCR negative day 2), 1 left hospital and 1 stop HCQ due to nausea/vomiting
- 70% of HCQ pts cleared their virus vs. 12.5% of controls
- 100% of HCQ/AZ pts cleared their virus vs. 57.1% HCQ only pts
Dr. George Martin: Although it was a small study, HCQ when dosed at 200 mg TID x 10 days results in significant clearance of the SARS-CoV-2 viral load in the nasopharynx of COVID-19 patients compared to non-treated controls. This effect is enhanced by the addition of azithromycin (dose not specified but usual dose is 250 mg per day). Of significance is that patients with advanced disease may have their disease rapidly progress while actually becoming PCR negative for SARS-CoV-2. As in all therapies, early intervention is critical.