New Drugs and Therapies for 2016: Foams
Drs. Neal Bhatia and Ted Rosen
Part 1 of an 8-part series on the large number of new topical and systemic medications that have become available or moved closer to approval in the last 12 months.
Patients love foams and several new ones entered the market during the past year.
Azelaic acid (AzA) for treatment of mild to moderate rosacea
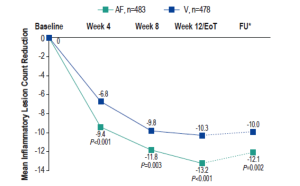
Reduction in inflammatory lesions with AzA foam.
AF, azelaic acid foam; V, vehicle
Draelos ZD, et al. Cutis. 2015;96:54-61.
AzA is used for the management of rosacea and a new 15% foam formulation (Finacea®) has been shown to be safe and effective for papulopustular rosacea (PPR). This new formulation was shown to be significantly superior to vehicle for the co-primary efficacy end points of treatment success according to investigator global assessment (IGA) and the nominal change in inflammatory lesion count from baseline to the end of treatment in patients with PPR (Figure 1). This new AzA formulation is also well tolerated and provides another option for patients with PPR that will help dermatologists match needs and preferences of individual patients and skin types with appropriate delivery modalities.
Calcipotriene 0.0005% and betamethasone dipropionate 0.064% foam
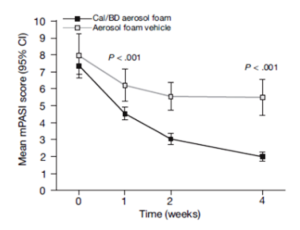
Percentages of patients achieving PASI 75.
Cal, calcipotriene 0.0005%; betamethasone dipropionate 0.064%
Leonardi C, et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:1468-1477.
A new foam formulation of calcipotriene 0.0005% and betamethasone dipropionate 0.064% (Enstilar®) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in December of 2015. It provides plaque psoriasis patients a new treatment option in an “elegant” vehicle that provides rapid relief from symptoms of this disease. In the pivotal phase III trial for Enstilar, over half of patients treated with the new foam were clear or almost clear according to IGA by week 4 (Figure 2). In addition, >50% of patients achieved PASI 75 with Enstilar. This foam was more effective than the ointment fixed combination of calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate as well as the individual components used alone in an additional phase IIa study.
Econazole 1% foam for Tinea versicolor in patients with skin type VI
Tinea versicolor is a common superficial fungal infection of the stratum corneum caused by lipophilic yeast of the genus Malassezia. The fungus interferes with the normal pigmentation of the skin, resulting in small, discolored patches that may be lighter or darker in color than the surrounding skin. Econazole nitrate is a broad-spectrum topical antifungal with activity against a variety of dermatophytes and yeasts. A new topical dosage form, econazole nitrate topical foam has been developed for treatment of interdigital tinea pedis and tinea versicolor and it has been shown to be effective for both indications.

